Case Organization
Brief explanations on the evolution algorithm parameters are given here.
A thorough understanding of them helps the proper selection but the best
combination of them is not known a priori and not required in order to obtain
an acceptable solution. A newcomer to the field of evolutionary optimization
may be overwhelmed by the great number of settings available but these are
necessary for the experienced and advanced user as they allow the definition
of every aspect of the evolution and fine tune the algorithm for a specific
problem. To facilitate the newcomer several presets are available with the
default installation. Additionally, most selection fields are briefly
described by tooltip popups.
The optimization features are grouped in six tabs, which appear in logical
sequence, beginning with basic settings and ending up to the optimization's
tab. Here we refer to the first tab, i.e. Case Organization.
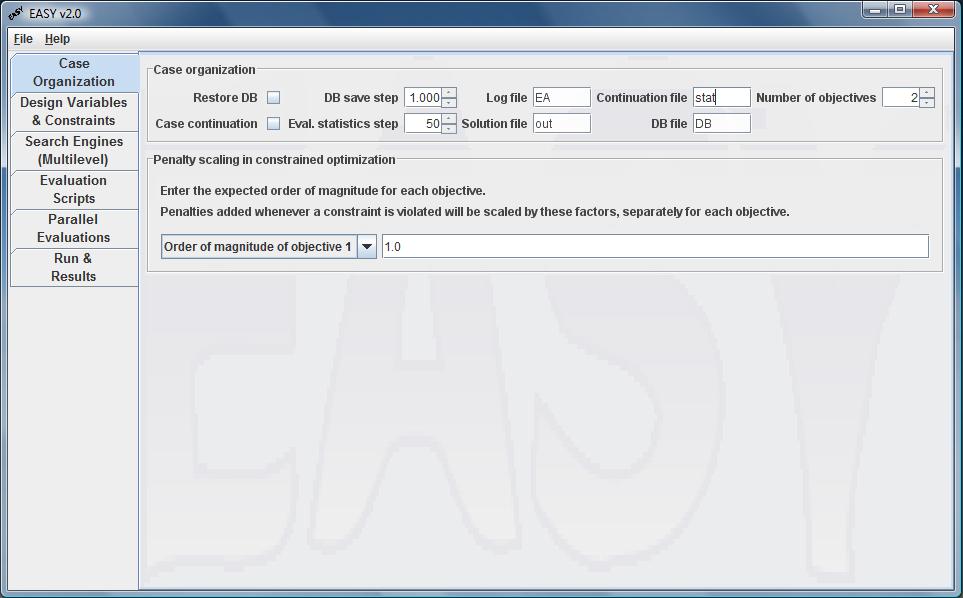
This tab controls basic settings of EASY such as the handling of the Database
of previously evaluated solutions, the possibility of continuing a
temporarily stopped optimisation run, the printout of optimisation statistics,
the definition of some result data files.
The number of objectives and scaling factors for the imposed constraints
should also be defined here.
The existence of a Database file (DB) intends to
avoid re-evaluating individuals, especially in case of time consuming
evaluation tools.
The Restore DB box allows EASY to initialize with an existing
database. This option is implicitly selected when continuation is performed.
If the Case Continuation box is checked, EASY assumes that a previous
optimization has been done through EASY and the user desires to continue from
the point it stopped. To perform a successful continuation, the database and
the state files should exist in the current working directory.
In the Number of Objectives box, the user selects the number of
criteria to minimize.
By selecting the Evaluator Statistics Step, the user is able to
observe several statistic features for the evaluator used in each
optimization level, during the evolution.
The database is saved with a user specified name in the DB file
textfield according to the value introduced in the DB Save Step box.
Information about the evolution is saved in the Log file.
The contents of this file are displayed while running the algorithm,
when zero Eval. Statistics Step is defined.
The Continuation file keeps the state of EASY in order to be able to
continue from this point. The final solution(s) is stored in the file
specified in the Solution file box.
Finally, in the Penalty scaling in constrained optimization box,
the order of magnitude for each objective is filled. This is just an
estimation the user can always make and whenever a constraint is violated,
the 'real' objective function value is replaced by a penalized objective
function value. For this purpose, penalty functions are automatically
defined by EASY v2.0.
|
